Picking and packing of cultivated mushrooms, mushroom products
Author: András Geösel
Picking of button mushrooms
Cultivated mushrooms contain 90-92% water and they do not have any evaporation regulating systems like for example plants. Ensuring that cultivated mushrooms get to the consumers in high quality starts at picking and assorting. Since mushrooms are very sensitive, delicate products, they have to be handled carefully, and should only be touched once during picking.
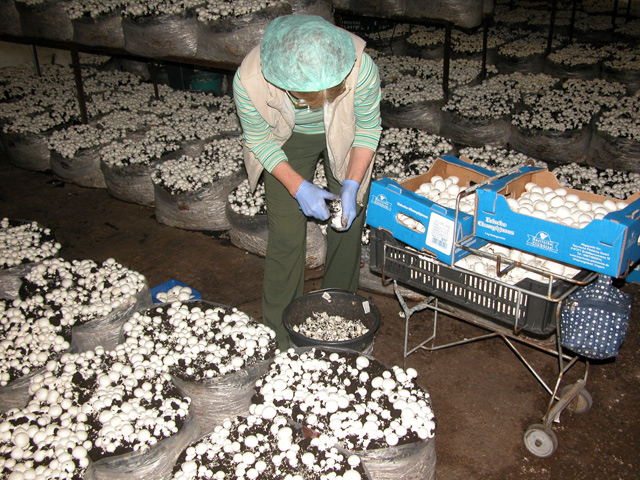
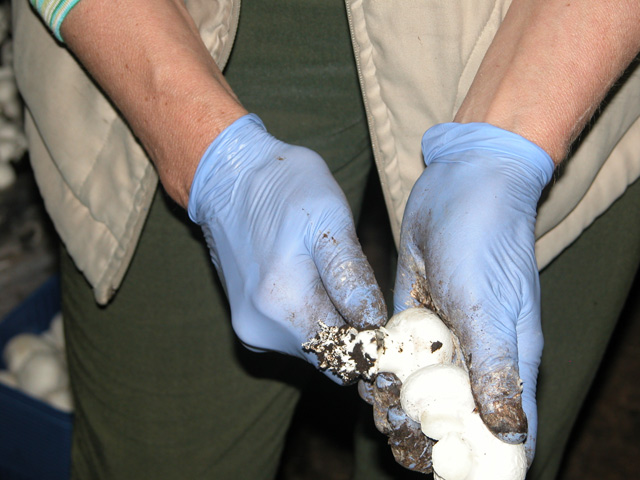


Picking of button mushrooms. Removing the base of the stem
Anywhere a fruitbody is touched, a brownish spot appears 1-2 days later. Pickers (who in Central Europe are mostly women) need training to learn how to handle mushroom with the most possible care, since the quality of picking could determine the quality of the final product. One type of damage is caused if the mushrooms are squeezed or touched more than once, the other type is when by removing the fruitbody, pickers damage the young, still developing mushroom initials, which then die.
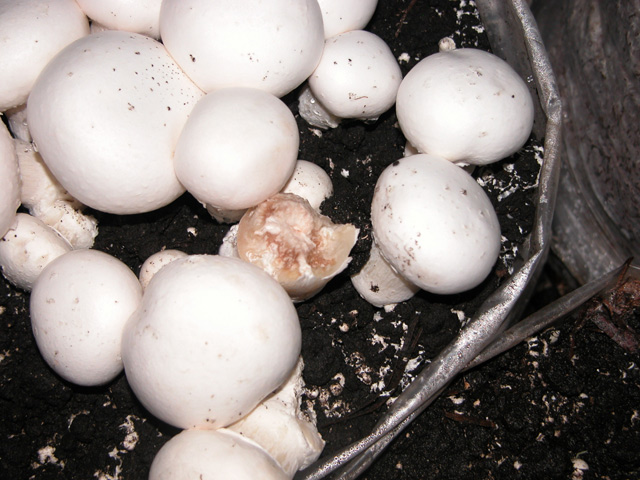

Secondary infestation of fruitbody initials damaged during previous picking
Mushrooms are picked, assorted and packed in one step, at the same time to minimize handling. The mushrooms are either placed into plastic boxes of different sizes following assorting by size, or they are put into bigger paper containers without classification. Depending on preference, the boxes or containers can hold mushroom between 100 and 500 g. In order to shorten the process, pickers usually pick only one size (one category), this way assortment do not take any extra time.
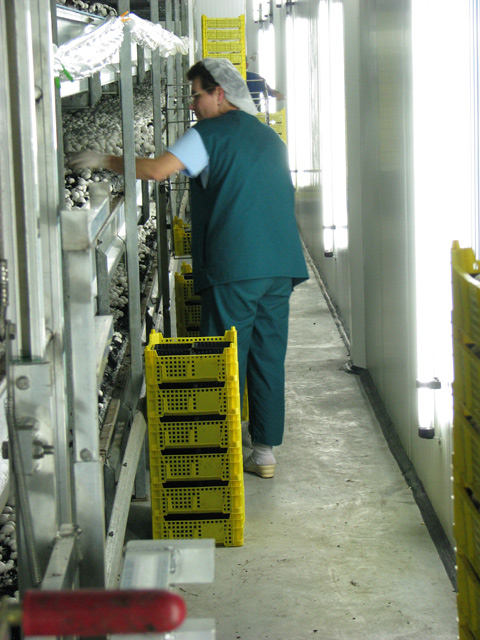
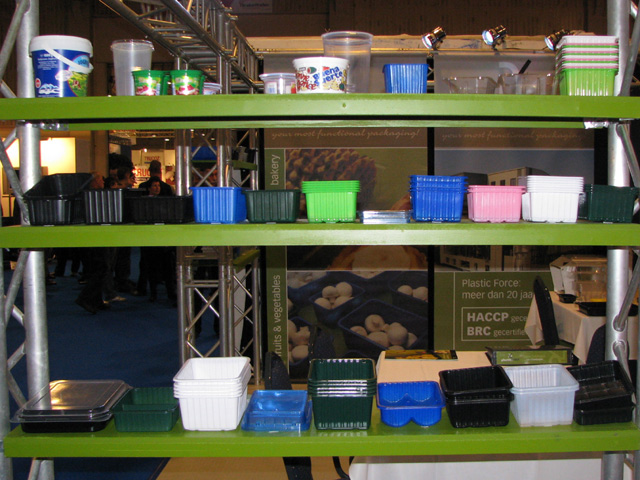


Picking in a Dutch type mushroom house. The different types of boxes and containers available for traders
Picking is generally done manually, although there are special machines available. These machines are used only in Dutch type houses, where “uniform” mushrooms can be grown, and the difference in fruitbody maturity of the same flush is only minimal. For manual picking producers prefer longer flushes. Spawn producers provide special strains for machine picking, which have longer and tougher stems. A higher than optimal CO2 level further aids longer stems to form.
Button mushroom picking machine
The quality of mushrooms deteriorates quickly. Besides picking, the way of packing and transportation also influence how long the product can be stored and kept fresh. An unbroken cold chain has high costs, but is essential in mushroom production.
Mushrooms cannot be kept together with any kind of vegetables or fruits in the same cold store; neither should they be shipped together in refrigerator vehicles. The reason for that is the fact that sensory characteristics of mushrooms alter after they were stored together with e. g. onions, pears or apples, while the storability shortens as well in case of mushrooms.
Quality grades of button mushrooms
There are certain quality standards of button mushrooms in Hungary and in the EU. These standards have to be applied for each type (cream or white) of button mushrooms sold fresh on the market. For food industrial purposes (canning, drying or cold storage) other regulations are in force.
In most cases, with special knifes pickers cut the base of the stem (which is contaminated by casing soil residues) during picking. There are mushrooms available on the market (e.g. in France and Spain) which are not cut, and still have the full stem with the casing residues on them, but it is not a common product. For 25 years, only cut and clean mushrooms can get to the consumers in Hungary.
The cut ends have to be smooth and perpendicular to the stem.
Fresh button mushrooms are marketed in the following developmental stages:
- closed cap – the cap is completely closed, the gills are not visible
- slightly opened cap – the cap is thinner, but a veil is still visible between the cap and the stem
- partially opened cap – the cap is opened, but its edge is still curved downwards
- opened cap – the cap is completely opened and straight
In each stage, the regulations and quality standards are the same. The mushrooms have to be:
- healthy – no sign of infections, the cut surface of the stem is not brown;
- clean – no contamination (with the exception of casing soil residues) or foreign matter;
- fresh looking – especially in case of open cap fruitbodies the gills have to have a color typical for the strain
- free of pests and pathogens;
- dry;
- free of foreign tastes and odor.
There are three quality grades of fresh button mushrooms in the EU: Extra, 1st class and 2nd class. The categories differ in color, shape and cleanliness. For example: the presence of casing soil residues or watery stem is only accepted in case of 2nd class mushrooms.
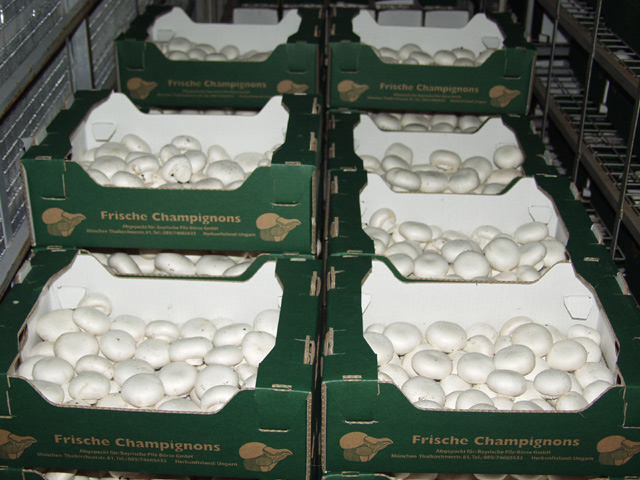


“Extra” button mushrooms packed in paper boxes and 2nd class mushrooms in plastic boxes
Categorizing by size is done by measuring the cap diameter. The smallest category in case of closed, slightly and partially opened caps is 15 mm, while opened cap mushrooms (grill mushrooms) have to be at least 20 mm, although practice shows that 2 cm opened cap mushrooms can neither be produced nor marketed. It is more common to grow muck bigger, 10 cm in diameter grill mushrooms.
Size categories of closed, slightly and partially opened cap mushrooms
-
Cap diameter
Maximal length of stalk
Size
Category
small
15-45 mm
Half of the cap’s diameter
medium
30-65 mm
large
above 50 mm
Size categories of closed cap mushrooms
|
Cap diameter |
Maximal length of stalk |
|
|
Size |
Category |
|
|
small |
20-55 mm |
2/3 part of the cap’s diameter |
|
large |
above 50 mm |
|
Each box or tray has to contain uniform products: mushrooms of the same color, developmental stage, condition, quality and size. The packages have to contain the same amount (weight) of mushrooms. Cream type and white button mushrooms can be mixed and put together in the same box, but only if their quality is the same. Fruitbodies on the top have to be in the same condition as those on the bottom of the pack (and therefore not visible until the pack is opened and all the mushrooms are taken out).
The package should provide proper protection for the mushrooms. Each material that comes into contact with the product should be new, clean and should not alter the quality of the mushrooms. Using stamps or stickers on the packs are allowed, but only if the ink and glue do not contain any harmful ingredients.
The following data have to be shown on each pack and container:
- the name of the product;
- the name of the trader and packer;
- place of origin;
- expiry date.
The picked mushroom has to get into cold storage within 3-4 hours. Cooling and packing are one of the most significant expenditures in case of fresh mushroom production. The temperature of mushrooms that get out of the growing room after picking is around 16-18˚C, which has to be lowered to +2˚C in 20-80 minutes. Since the fruitbodies do not have any evaporation system, cooling has to be done with special attention to optimal relative humidity. In order to prevent water (and weight) loss in the mushrooms, the recommended humidity level is 94%. First the freshly picked mushrooms are cooled down to 8˚C in 15-20 minutes, which followed by further cooling to +2˚C, what the optimal storage temperature is. The mushrooms are kept in the main cold store on +2˚C, in 92% relative humidity until packing is done.
In the packing area, mushrooms are placed into boxes or trays, weighed, then wrapped. The smaller boxes are then put into containers. Special packs or baskets of mixed mushrooms (cream type and white button mushrooms, oysters or shiitake are put together in a box with a bit of parsley for decoration) are also prepared.
The ambient conditions in the packing area are regulated as well. The air temperature is 10-12˚C and the relative humidity is 55-60%. Any other values would result in condensate forming inside the polyethylene used for wrapping, which could cause bacterial infections (Pseudomonas tolasii) on the surface of the mushrooms in 2-3 days. The containers are then loaded into refrigerated vehicles. The cooling chain should never brake, or else the products warms up and condensate forms.
Packing button mushrooms in small scale: weighing, equalizing, quality check, packing, wrapping and labeling
Packing button mushrooms in large scale
For quality control, the temperature is monitored, adjusted and recorded in the refrigerated vehicles during the entire transportation period. In case of a well-organized system, the fresh product should get to the consumer within 24 hours, and then it can be cold stored for 6-7 days.
Quality regulations of fresh oyster mushrooms
Oyster mushrooms are picked manually. After removing the mushroom from the bags, pickers cut the base of the fruitbodies, which is contaminated with substrate residues. Oysters are picked before they become fully matured, thus they can be kept in a better quality. Another reason for not waiting until the mushrooms mature is that cultivated hybrid oysters produce excessive amount of spores, which cause allergic reactions. By using “Spoppo”, which is an oyster strain with a low spore count, this problem can be avoided.
Quality standards of oyster mushrooms:
- the cap should have a color typical of the strain,
- the edge of the cap have to tilt slightly downwards, it should not be cracked and should not contain any spore residues on the surface,
- there cannot be any signs of bacterial infections or damage caused by pests on the fruitbodies,
- the mushrooms should not be contaminated by any kind of foreign matters, straw residues, soil or dust.
Quality grades and packing
Oyster fruitbodies are sold either together or separated.
Whole fruitbodies should have:
- almost all of the stem, which holds the fruitbodies together,
- caps with an average at least 4 cm in diameter (but some can be smaller or bigger),
- stems that are not too long.
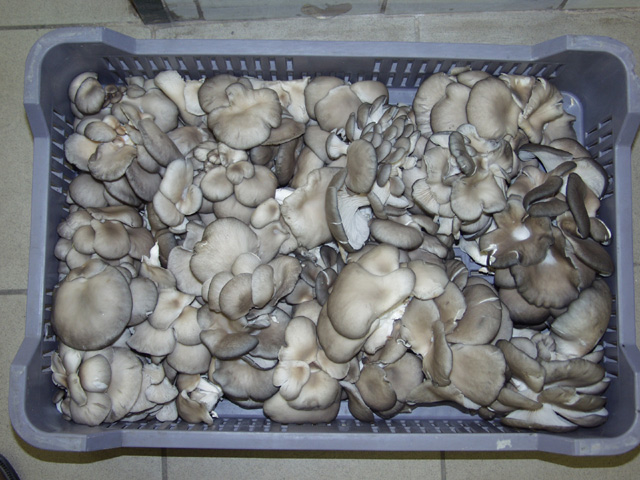

Whole oyster mushrooms in plastic container for inland markets
The individual fruitbodies can also be separated and sold sorted by size (diameter). This case the stem is cut shorter and same sized caps are placed together in paper or plastic boxes or on trays.
Individual fruitbodies should:
- have stems no longer than 1-3 cm,
- be placed with same sized (from 5 to 10 cm) caps together.
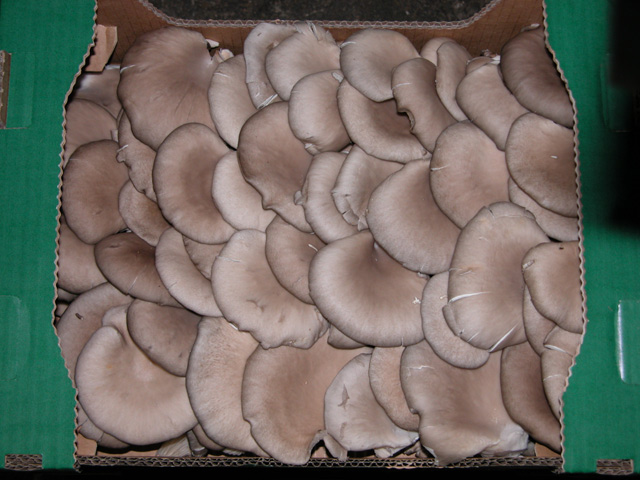

Individual oyster caps packed in paper box
The stems that were removed during the process are sold for making soup mixes. This latter type of oyster has higher price, since they are kitchen ready and do not require additional cleaning (with the exception of washing). The costs of picking, packing and storing are the same as presented in case of button mushrooms.
Quality regulations of shiitake
Shiitake fruitbodies have to be picked before the edge of the cap straightens. Similar to button mushrooms, shiitake is removed from the substrate block by a gentle twist, and then the base of the stem is cut by a sharp knife. First grade shiitake have 60-80 cm caps maximum, while the stem is not longer than 20 mm. Each type of packing (box or tray) should contain mushrooms in the same size. Shiitake can be stored longer than button or oyster mushrooms and they tolerate transportation better. Dried shiitake is exported into Europe and other parts of the world from the Far East. Fresh shiitake is produced then sold locally.
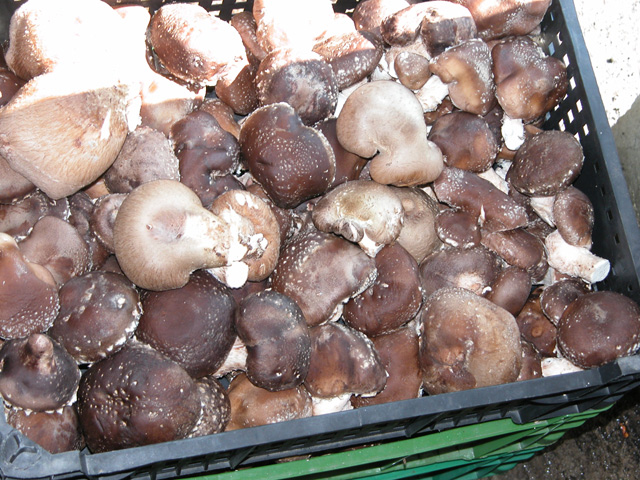

Fresh shiitake mushrooms placed in a plastic box
Processed mushroom products
Not only the fresh, but the different types of processed mushroom products are popular amongst consumers as well. One of the products sold in the highest amount are sliced mushrooms.
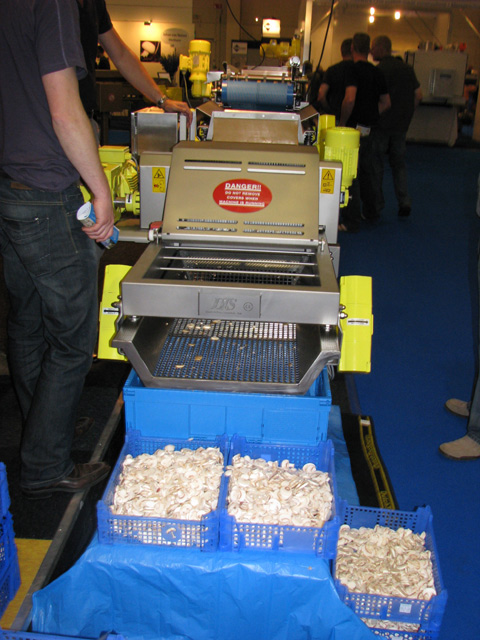

Mushroom slicing machine
The mushrooms are washed, sliced and packed by a special machine. Strict regulations are in effect, since producing sliced mushrooms is a type of food production. Nowadays slicing machines are used in Hungary as well, as selling these kinds of products also contribute to the extension of the market. (Another solution is to provide products with value added – so called functional foods –, such as vitamin D enriched mushrooms.)
Preservation
As mentioned earlier, mushrooms are sensitive products and cannot be stored for longer than one week. Mushrooms are no longer just seasonal products (like most vegetables and fruits), but can be bought any time of the year. Although fresh mushrooms are available, canned or preserved products have their fair share from the market at all time. Not only hotels, restaurants and caterers need canned mushrooms, but average consumers as well.
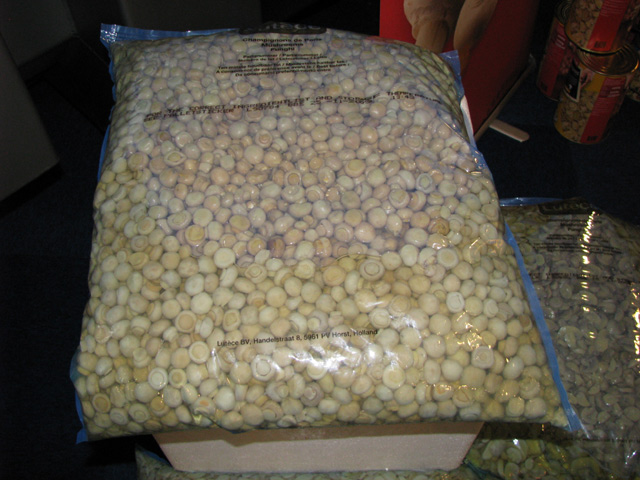

Preserved mushroom in a 10 kg bag
The main mushrooms preservation methods are the following:
- freezing
- canning
- drying.
Mushrooms are often dried and sold whole, sliced or chopped, and even powdered. Powdered mushroom are ingredients of soup mixes, pates and creams or sold as spice (e. g. boletus). One (quite expensive) way of drying mushroom is lyophilization. Lyophilized mushrooms keep their original color, odor and taste better than those that have been dried by traditional methods.
Mushrooms can be preserved by pickling, salting, lactic fermentation and marination. Traditional methods include preservation in fat and by smoking. The latter adds a characteristic taste to the product and because of the loose structure of the mushroom smoking process does not take long time to complete. Frozen mushroom products are also popular amongst consumers. Depending on the preparation processes prior to freezing (slicing, chopping, spicing etc.), these types of products are mostly kitchen ready. Another direction of mushroom preservation is to use them as special ingredient to products which normally do not contain mushrooms. Mushroom flavored chocolates, coffees and vinegar can be bought in the shops of bigger supermarket chains.
Mushroom based medicinal products have to be mentioned here as well. Many types of pills, powders or extracts of various medicinal mushrooms are available all around the world. Since experiments proved the positive effects on dermatological problems (sunburn, burn, aging), mushrooms are used in creams and other cosmetic products. Mushrooms are not only consumed, but they are also used for decorative purposes (Ganoderma species in floral arrangements) and as materials of clothes or hats (popular in Mid-Europe and Transylvania).
Due to various ways to preserve mushrooms, both wild grown and cultivated mushrooms are available for the consumers any time of the year.
Canning process
In Hungary, mainly those mushrooms are used for canning that have lower quality and cannot be sold fresh. Due to expensive manual work (mainly picking), producing for the canning industry is not cost effective, and is only done in certain West European farms, where the mushrooms are picked by machines. The canning process of mushrooms is shown here.
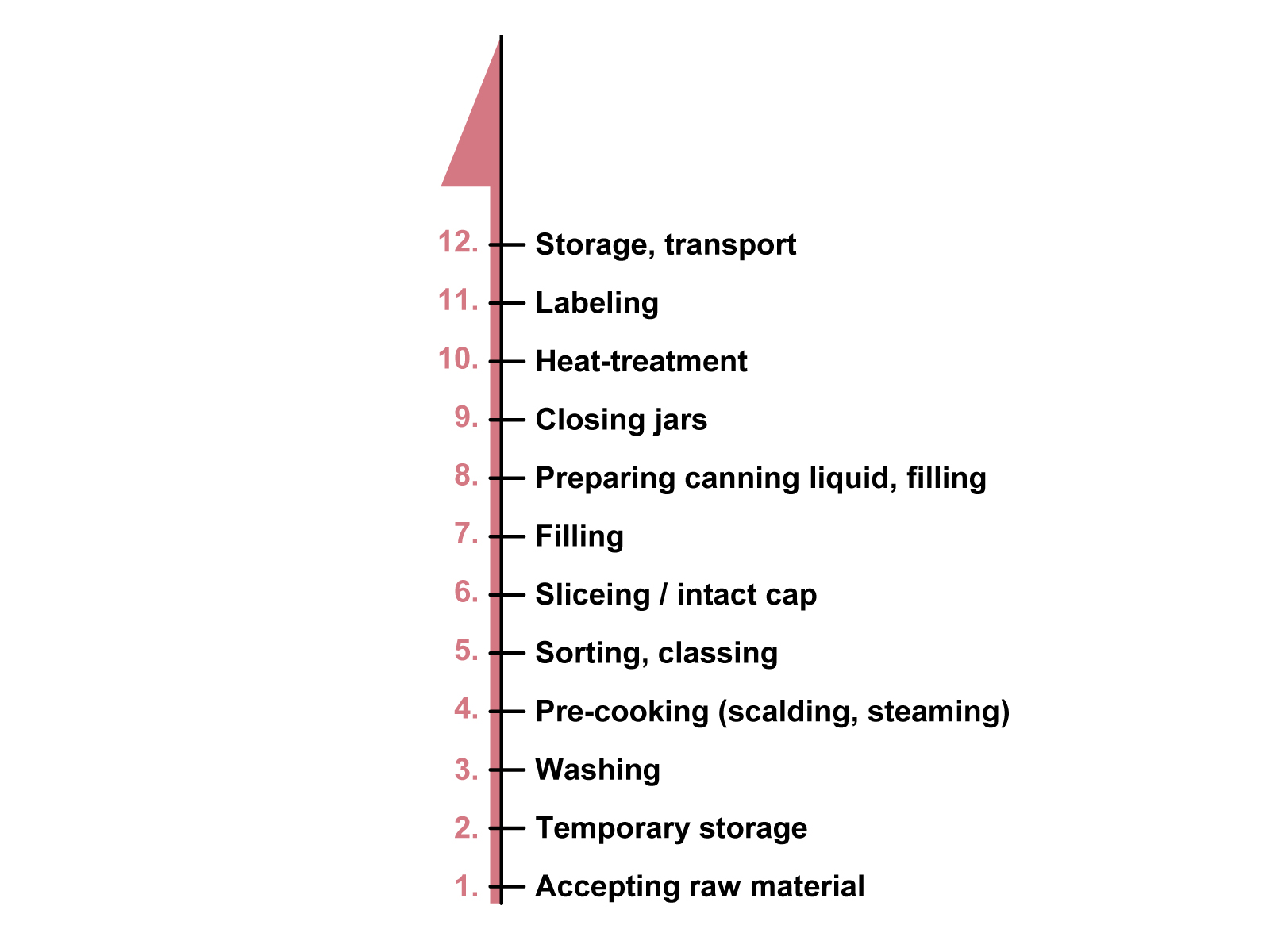
Draft of the mushroom canning process
The fruitbodies are washed first, and then they are pre-cooked or pre-steamed. Next the mushrooms are sorted and graded if necessary. Mushrooms are placed into cans or jars sliced or whole, then the cans or jars are filled with water, which usually contains salt and sometimes different spices. After closing them, the product is preserved by heat treatment.
Since these procedures are special types of food production, strict regulations are applied. The processes are monitored, the conditions (temperature, time etc.) are registered and samples are taken at many points for chemical and microbiological examinations. A tour of a Polish canned mushroom company is available on the following link.
Check your knowledge!
- What are the steps of mushroom preserving?
- What quality grades of button mushrooms do you know?
- Describe the “Extra” quality grade of button mushrooms!
- What kind of processed mushroom products do you know?
- Give a short description of mushroom picking!
References
Győrfi, J. (2010): A csiperkegomba (Agaricus bisporus) termesztése. (In: Győrfi, J. (szerk): Gombabiológia, gombatermesztés. Mezőgazda Kiadó, Budapest, 139-187.
Kovácsné, Gyenes M. (2010): Laskagomba-fajok (Pleurotus spp.). (In: Győrfi, J. (szerk): Gombabiológia, gombatermesztés. Mezőgazda Kiadó, Budapest, 226-263.
Kovácsné, Gyenes M. (2010): Shiitake (Lentinula edodes) termesztése Laskagomba-fajok (Pleurotus spp.). (In: Győrfi, J. (szerk): Gombabiológia, gombatermesztés. Mezőgazda Kiadó, Budapest, 273-300.
EC Regulation No 1863/2004. Laying down the marketing standard applicable to cultivated mushrooms. Official Journal of the European Union. L 325/23
Hyde K. D., Bahkali A. H., Moslem M. A. (2010): Fungi—an unusual source for cosmetics. Fungal Diversity, 43: 1–9.

