National and international importance of medicinal and aromatic plants and their production
Author: Jenő Bernáth
History of the development of Hungarian medicinal and aromatic plant sector
For centuries, the medicinal and aromatic plants were collected or cultivated in the territory of Hungary for domestic consumption, mainly. Even the representatives of the Hungarian nation that came in the Carpathian basin utilized some medicinal plants; however the curing procedure could have been mixed with many forms of superstitious elements. Some of the ancient local name of the plant species (witch-pulp, devil-costae root, devil-grape, etc.) shows that. Later on, the elements of Christianity appeared in the name of the local medicinal plants (Tree of the God, Jesus-nettle, Assumption-rose, Assumption-mint, etc.).
In the territory of Hungary, the first written records of medicinal plants date back to the middle ages and can be found in the manuscripts of the monks settled down here. Furthermore, number of medicinal plants were introduced at that time into the Carpathian basin and cultivated in the gardens of monasteries or noblemen (for instance some members of Lamiaceae family). However, the large-scale production of medicinal and aromatic plants started in the middle or in the second half of the 20th century, only. Parallel with large-scale production the primary processing of plant material and distillation of essential oil-bearing plants were introduced. The scientific background for the development of the section was provided by the activity of Hungarian scientist, Páter Béla (1860-1938) who was the first director of the Research Station of Medicinal Plants.
The lack of medicines, due to the First Word War, called attention to the medicinal and aromatic plants. Therefore, by the decree of Agricultural Ministry the Medicinal Research Station was established at Kolozsvár in 1915. In the first years, the Institute managed the control of collection and cultivation of medicinal plants and later on was involved into the research-development projects of the section.
After the period of the First Word War - mainly based on the activity of Research Station of Medicinal Plants – Hungary became a country of “Great Power” in the field of medicinal plants. It became obvious in both the large production of dried plant drugs and production of essential oils. Beyond the increase of local consumption large amount of the Hungarian medicinal plant products appeared in the West-European market. As a part of the dynamic development of the medicinal plant sector János Kabay invented a word patent for extraction of dry-poppy capsules and established a new pharmaceutical factory, known as Alkaloida, even nowadays.
The industrial production of essential oil was started in the 20s of the 20th century. The large-scale cultivation of peppermint (Mentha piperita) and the two lavender species (Lavandula intermedia, L. angustifolia) were introduced in the large-scale production by the help of foreign propagation material. The remains of the first lavender plantation on the southeastern slopes of the mountains of Tihany peninsula, which has a submediterranean climate, can be seen even nowadays. Until 1941, the production of peppermint oil reached the 8500 kg. From the two lavender species 400-600 kg essential oil was produced by the industry. From the other species the production of dill oil worth to mention with 2000-3000 kg value. Among the collected species, the chamomile got a world-wide appreciation and became a Hungarian national product.

The remains of the first lavender plantation on Tihany peninsula (Fotó: Bernáth)
After the end of the Second Word War, as a consequence of the permanent lack of medicines and teas, the research activity concerning the medicinal and aromatic plants accelerated and the modernization of the cultivation and processing methods has started. By that time, under the leadership of the outstanding scientist Miklós Békésy, the sclerotium production of Claviceps purpurea was introduced into the practice by artificial infection, and the large-scale cultivation of Digitalis lanata opened. In addition, the intensification of the research activity on Vinca and steroid sources and production of plant-raw contributed to the further development of Hungarian pharmaceutical industry.
Because of the new tendencies that appeared in the production of plants and their products the former, world-wide appreciated structure of the medicinal and aromatic plant sector has changed in a great deal. The production of raw and processing of the products - because of administrative and guidance-technical considerations - separated into three production areas. The three areas were as follows:
- Collection, cultivation, processing and marketing of medicinal and aromatic plants on a limited scale (integrated into the commercial area),
- Production and processing of medicinal plants on a large scale (integrated into the agrarian-area)
- Large scale production of industrial crops (organized and processed by pharmaceutical industry)
Until the first half of the 90s of the 20th century the medicinal and aromatic plant sector became one of the outstanding fields of Hungarian agriculture (Hornok, 1978; Hornok, 1990; Bernáth, 2000). The products of the sector were sold on the world-market as special Hungarian products. At that time the cultivation area of medicinal and aromatic plants ranged between 37 thousand and 42 thousand hectares. The amount of dry plant raw was as much as 35-40 thousand tonnes yearly. The estimated USD income reached 35 millions. However, owing to the changes of the Hungarian statistical evaluation system, no estimable data are available in connection with the actual productivity of medicinal and aromatic plant sector.
Traditional regions of production in Hungary
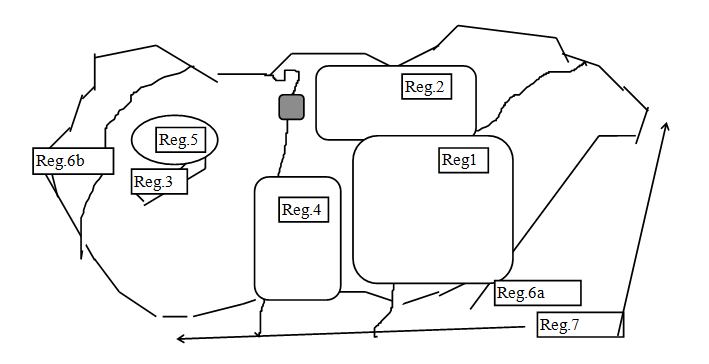
We have information about the formation of the regions, which were specialized in collection and cultivation of medicinal plants from the beginning of the 20th century. The development of regions was based on biological and economical features of Hungary to increase the export-oriented production of medicinal plants. The formation was a spontaneous process, which could be characterized with number of rational elements. As a result, during the last 90 years, special collection-cultivation-processing regions appeared in Hungary – which are under disorganization at present - but they influence the sector even nowadays. The figure shows the seven production regions, which separate more or less from each other geographically.
Main regions of Hungary specialized for production of medicinal and aromatic plants (Bernáth, 1998b)
(Reg.1.- Great Plain; Reg.2. – North Hungarian Mountains; Reg.3. – Balaton Uplands; Reg. 4. – South of Hungary; Reg.5. – Bakony mountains and surroundings; Reg.6a – Countryside specialized for the production of „spring” poppy; Reg.6b - Countryside specialized for the production of „autumn” poppy; Reg.7. – species cultivated without regional restriction
Regions for utilization of the natural flora
The development of collection and processing of chamomile (Matricaria recutita) flower in the Great Plain of Hungary (Reg.1.) is a good example of the utilization of the local flora. The formation of the region was generated, even in the last century by the increasing demand of German market. The flower of chamomile (Chamomillae flos) was produced in this region as a special Hungarian product from the beginning of the last century, however it was known as „German chamomile” in the world market because of the central role of German merchants in distribution (Bernáth and Zámboriné, 1999). The outstanding quality of Hungarian chamomile, which was at first supported by empirical observation and proved later on by up to date analytical measures, due to the special ecological circumstances of the region. Both organoleptic and chemical features of the drug – which comes from the saline soils, which cannot be utilized for any other crops - guarantee the first class quality. For processing of chamomile and some other species, which grow around the region (Achillea collina, Juniperus communis, Crataegus spp. Sambucus nigra, etc.) the factories were installed in villages and towns situated in the merge of the region (Hajdúböszörmény, Füzesabony and surroundings, etc.). In the season of blooming, even nowadays, some thousand people join in the collection of chamomile to produce the valuable drug of the plant which is registered in the EU as special Hungarian product.
The second region (Reg.2.) developed in the North Mountain region of Hungary and its surroundings for utilization of the natural flora, too. In this region the collection and processing of rose hip (Rosa canina), black elder (Sambucus nigra), blackthorn (Prunus spinosa), hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) and other forest-grown species are going on. This region has a very valuable biological potential and furthermore coincides with large amount of labour supply, which can be the basis of its further development.
Regions specialised for agrarian production
In the formation of the regions specialized for agrarian production beyond the spontaneous elements the importance of biological and economical considerations increased. As an example for the cultivation of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia), which is a xerophilous species, the warm slopes of Tihany peninsula were selected in the period between two Word War (Reg.3.). The submediterranean climate of Tihany peninsula provided suitable ecological conditions for the high productivity. The remains of the original stand, which was planted in 30s of the 20th century, can be seen, even nowadays (‘ancient-plantation’). In the case of following plantations the farmers took into consideration of the adequate ecological condition of the Lake Balaton and locations at Balatonakali and Daránypuszta were chosen for plantations.
The next production region (Reg.4) was established in the southern part of Hungary nearby Baja and Kalocsa for the production of xerophilous species of Mediterranean or subtropical origin, such as marjoram (Majorana hortensis) and basil (Ocimum basilicum). Both the yield and drug quality of these species proved to be the best in this region (Héjja és Bernáth 1998). Furthermore this region was a centre of red pepper production (that of the hop production formerly), which was equipped by drying and processing facilities for spice production. These processing centres provided good possibilities for processing of medicinal and aromatic plant species parallel.
From 60s to the end or 80s of last century, formation of a unique region, specialized for parasitic ergot cultivation (Reg.5.), was motivated by both ecological and economical considerations. The centre of the ergot cultivation was the rye production area of the south-western extensions of Bakony Mountains around Zirc and Nagyvázsony. In this area the production of ergot went on industrial scale with outstanding level of mechanisation and processing. Because of the incursion of the industrial non-parasitic fermentation of ergot alkaloids the importance of this region became extinct.
The production of poppy (Papaver somniferum) has a great traditions in Hungary (Bernáth 1998a and 1998b). It is due to the multipurpose utilization of the plant: the seed is an appreciated food in Middle-Europe, especially in Hungary and the dry capsule of the plant is sold for industrial processing to get opiate alkaloids. Based on ecological considerations the cultivation area of poppy was separated into two regions. The cultivation of „spring” ecotype is going on the Great Plain of Hungary and on some other countryside, suitable for production of poppy in spring vegetation cycle (Reg.6.a). However, in former time the production of ‘autumn’ sown (winter) poppy concentrated into the Western countryside, where the winter climate is not so hard and the danger of the frost action is less serious (Reg.6.b). Because of the recent breeding of series of new ‘autumn’ poppy cultivars, which changed physiological property, the regional separation of the two ecotypes is not so decisive.
In contrast with above-mentioned regional separation there are a number of medicinal plants, which grow well in several part of Hungary, without any restriction. This region is not strictly specified and overlaps the whole territory of Hungary and can be characterized by the overall climatic circumstances of Carpathian basin (Reg.7.). Some of that species which can be cultivated under wide range of conditions are as follows: species from the Apiaceae family (Foeniculum vulgare, Carum carvi, Anethum graveolens, Coriandrum sativum, Pimpinella anisum etc.), mustard (Sinapis alba and Brassica spp.), milk thistle (Silybum marianum), oil pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo subsp. pepo convar. styriaca) etc..
Spectrum of medicinal and aromatic plants in Hungary and its expansion
The spectrum and the amount of the consumed medicinal plant drugs are enlarging year by year, worldwide. In former time two regulations defined the official list of medicinal and aromatic plants in Hungary (the 8th Hungarian Pharmacopoeia being in force until July of 2006, and the Decree of Government No. 203/2002(IX.14) on the medicinal plants being present in retail trade). The two lists overlap each other in many cases. Since the time of adherence to EU the official number of medicinal plants increased enormously. In the 8th Hungarian Pharmacopoeia (2004), which was compiled taking into consideration the articles of European Pharmacopoeia, the number of medicinal plants doubled (Szendrei and Csupor, 2009). The number of drugs of plant origin in Hungarian Pharmacopoeia increased up to 160, the number of essential oils up to 34, the number of fatty oils up to 20. Furthermore 11 plant extract took place among the official articles. The increase of official Hungarian articles containing materials of plant origin can be explained with two facts: some of the medicinal plants were part of the former European practice and we accepted it, secondary the effectiveness of many plant species were proved by scientific methods in the last two decades (Anthemis nobilis, Eleutherococcus senticosus, Ginkgo biloba, Silybum marianum, etc.). Additionally, some species, which effect are less known for Hungarian consumers, appeared in the Pharmacopoeia (Eucalyptus spp., Panax ginseng, Passiflora incarnata, etc.). In the case of the above mentioned species the quality control instructions of Pharmacopoeia guarantee the safety of the drug consumption. There are much more risk if we would buy drugs in retail market sold according to the list of Government Decree (203/2002 (IX.14), or according to any other food regulation. The reason that the Decree of Council of Ministers signed in 1976, as well as the Hungarian Quality Standards, which identified the quality of medicinal plants were withdrawn. It does mean that at present the quality control of medicinal plant drugs are not regulated well and is going on unpredictably. The hope for the solution is the preparation of the specific chapters of Codex Alimentarius, which is in progress, recently.
Worldwide enlargement of production and consumption of medicinal and aromatic plants
The utilization of natural products of plant origin came into the centre of interest in the last decades. The status reports of the International Organisations support this fact (UNIDO, FAO, WHO, UNCTAD/GATT). According to the estimate of WHO, published in 2011, about 25 per cent of modern medicine contains materials of plant origin or has some chemical relation to the plant species, which were used in traditional medication. It is more obvious if we would analyze such therapeutic fields as cancer therapy, or microbiological infections. In these therapeutic fields the ratio of medicines of plant origin may reach the 60 per cent. According to the above-mentioned WHO document – beyond the countries, which utilize medicinal plants traditionally – in the majority of countries, which can be characterized by highly developed pharmaceutical industry, the application of alternative therapeutic methods increased dramatically. In Germany, 80 per cent of the inhabitants use medicine of plant origin at least once a year. The similar data in Canada is 70, in France 49, in Australia 48, in the United States 42 per cent. The acceleration of the consumption of products of plant origin was motivated by the fact that, owing to up-to-date research activity, new compounds were found for therapeutic fields, which cannot be cured by synthetics, even nowadays. The alkaloids of periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus), which cure the leukaemia, the immune-stimulant compounds of purple coneflower(Echinacea spp.), the geriatric compounds of ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba), the migraine killing parthenolides of feverfew ( Chrysanthemum parthenium) and the Cavinton synthesised from Vinca alkaloids belong to this group. Current success is the application of yew (Taxus brevifolia); its biological agents are rather active compounds in cancer therapy.
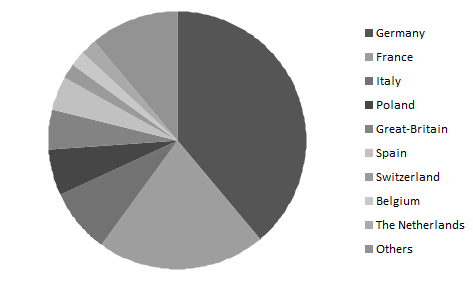
The application of alternative curing methods is increasing continuously and in the first decade of the 21st century, the world market of alternative medicines enlarged by 5-18 per cent. In Europe, the value of the alternative products sold is about 4 billion EURO, yearly. In Europe Germany is a leading country regarding the consumption of these products. About 39 per cent of alternative products are consumed here. The next country is France with 21 per cent share. In other countries the rate of consumption is less than 10 per cent.
Per cent ratio of European countries in consumption of alternative medicines of plant origin, which represents milliard EURO value, yearly (WHO 2011)
Main structural elements of medicinal and aromatic plant sector
Medicinal and aromatic plant sector consists of four structural elements, which are as follows: production of raw material, wholesale, retail trade and export. The figure shows the linkage of these four functions. These structural elements can be present in the activity of any firms separately or they can be present in joined form creating a complex system of activity. It does mean that in some cases the same firm (for instance Herbaria in Hungary) plays a role in production of medicinal plants, in their wholesale and retail trade and in export-import activity at the same time.
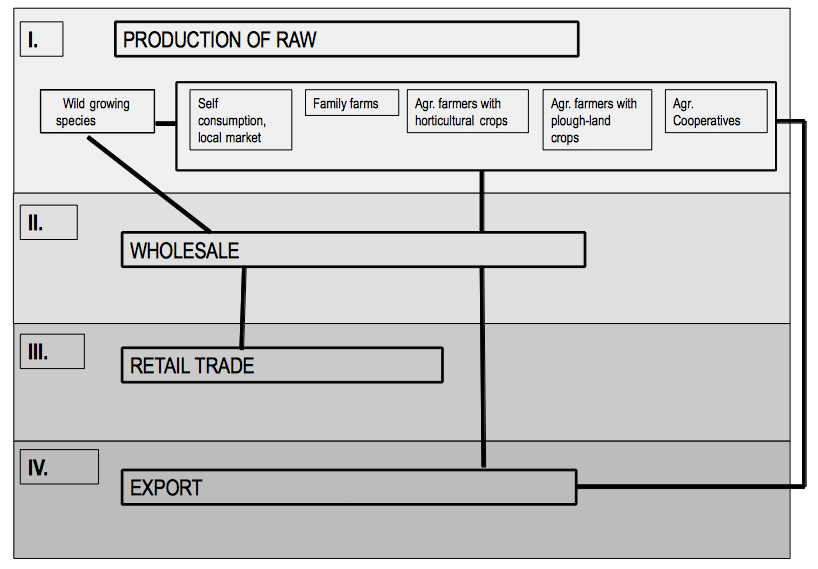
The four structural elements of medicinal and aromatic plant sector
I. First structural element: production of raw material
Even nowadays about 90 percent of 1200-1300 medicinal and aromatic plant drugs and products, which are present in the EU market comes from wild collection and is exported by developing countries. In Hungary 50 per cent of the of medicinal and aromatic plant raw material (5,000-8,000 tonnes dry drug) and about 60-70 per cent of medicinal and aromatic plant species come from the natural ecosystems. However, the importance of the cultivation, the production of the raw material in agrarian-systems will increase in the next decades. In Hungary the amount of drugs, which comes from agrarian-system is about 50 per cent of the total production; while in Germany 100 per cent comes from cultivation, even nowadays. In Hungary, the agrarian production, depending on the applied technology, type of ownership of the land and other circumstances, is going on in five different forms, which forms can work separately or in combined structure.
Production for domestic consumption or for the local market. It is a new tendency that the increase of interest for medicinal and aromatic plants motivates their local or garden-scale production. The majority of producers has a restricted experience in production of medicinal plant or has knowledge on overall agrarian crops, only. Consequently they have no special equipments and technology for the production and the quality of the product is uncertain. The outputs of this production form has a small influence on the total production of the medicinal and aromatic plant sector, but contribute to the increase of domestic consumption and to the circulation of the local market.
Family farms. In the family farms the value of the production is relatively high. In this production form plant species are cultivated by special methods and they need a lot of manual work and are cultivated in small areas. No developed technology is applied in the majority of cases. The spectrum of the plant species can change year by year in the family farms, depending on demand. Characteristic species cultivated in this production form are as follows: calendula, marjoram, thyme, valerian. However, we have to consider that more recently this production form of some of these species came to an end as a result of quick technological development and their intensive cultivation was started in Germany by large-scale technologies.
Agrarian producers with horticultural crops. From the point of view of ownership, the family farms and smaller farms belong to this production form. It is the advantage of this production form that the ‘ecological’ cultivation, which produce an increased value and is more and more preferred in Europe, can be best managed in this structure. The size of the horticultural farms specialized for production of medicinal and aromatic plants is at least 25-30 hectares or more. In the production structure of these farms the commercial crops are present too, to ensure the crop rotation. The spectrum of medicinal plants is selected taking into consideration the technical conditions of the farms as well as the possibilities of the coupling of plant cultures. According to the experiences, about 3-6 different medicinal plants can be cultivated in this production form, which give an acceptable and stable income. However, the optimal number of cultures depends on the local conditions.
For the reliable production, the farm has to possess special post-harvest technology, which is an important precondition of gainful function. For instance it is important to have dryers and cleaning equipments of appropriate capacity, and storage rooms. If they want to make products of higher value they need chopping machines, mills, even distillers for the processing of the essential oil bearing plants. The effectiveness of these facilities can be increased by the mechanization of material handling. Some characteristic culture of this production forms are as follows: mint, pepper-grass, lovage, tarragon, balm.
Partly belongs to this, partly to the next production form when the farm produces high quality drugs on the basis of special contract signed by national or foreign enterprises. In these cases the cultivation is going on taking into consideration the GAP recommendation worked out by the expert of consigner firm.
Agrarian producers with field crops. From the point of view of ownership, it can be the production form of the large farms, co-operatives and government farms. The crops cultivated in this form are well mechanized. All cultivation steps from soil preparation up to sowing, plant protection, harvest and post harvest procedures are made by machines. The size of each culture can be as large as 80-100 hectares. However, in the case of this production form, to get a stable income, cultivation of at least 3-6 species is advisable. The advantage of crop rotation can be utilized if other agricultural crops are also involved, which cultivation technology can be associated with medicinal plants. It is important to have appropriate drying capacity because of the large amount of fresh plant raw, which was obtained due to mechanical harvest. However, there are efforts world-wide for introduction of the methods of integrated cultivation system in this production form, but the introduction of “ecological” production seems to be out of reality. Some characteristic crops that can be cultivated in this production form are as follows: caraway, coriander, milk thistle, and safflower.
Modern agrarian co-operatives . It is proved by foreign examples, especially examples from the Netherlands and Denmark, that the farms specialised for farm like production of different crops do not want to deal with the whole-spectrum of innovation, cultivation, processing and marketing. It happens in spite of the fact that they have much better conditions of capital comparing to us. The farmers taking economical considerations join into special co-operatives. Under the aegis of co-operatives, many field of activity, including innovation, cultivation, processing of raw material and marketing, can be harmonized and optimized, economically. As a result of co-operation stable supply of high-quality propagation material can be guaranteed, the development of processing-technology becomes easier by concentrated installation, they can harmonize the marketing strategy and the promotion of their interest becomes more effective.
II. Second structural element: wholesale
In the medicinal and aromatic plant sector the wholesale activities includes different aspects of action, which are as follows: buying up the raw material, management of cultivation based on contracts, post-harvest processing, product manufacturing and marketing (including export activity). The wholesale activity until the first early 90s was a privilege of some firms in Hungary (Herbaria, Forest Product Company). This structure changed in a great deal because of overall political and economical changes. The number of firms involved in this type of activity multiplied in the first half of the 90s. However, the large number of wholesale companies generated an unexpected competition, which resulted in temporary harm of natural flora, incalculable amount of the drugs in the market and the decrease of drugs quality. As a result of the following concentration of capital the number of the wholesale companies decreased considerably adjusting to the size of the country. The large companies have about 1000 tonnes drug circulation /year, the smaller firms about 10-12 tonnes/year. The number of distributed drug specification can be as much as 100-200.
III. Third structural element: retail trade
The small-scale marketing of medicinal plant drugs and its products is going on in the units of retail trade. Before 1989 this activity was concentrated to the pharmacies of the Pharmaceutical Regional Centres and to the shops of Herbaria and Forest Product Company (20-25 retail trade units). From the 90s – parallel with the changes of regulations – there was an enormous increase in the number of shops selling drugs made of medicinal and aromatic plants. In many cases, the medicinal plant drugs are sold together with food products in groceries, too, as delicacy tea products. As the sellers usually do not have any experiences concerning medicinal and aromatic plants, sometimes product of uncertain quality, or even harmful products appear on the shelves. The situation is much more confusing if we take into consideration that the spectrum of the products increased enormously lately (medicinal plant teas, tea mixtures, phytotherapeutic products, dietary supplements, medicinal foods, cosmetics, etc.). However, the all-comprehensive and stable regulation of processing and trade of these products is lacking in Hungary.
VI. Fourth structural element: export-import activity
The export plays an important role in the activity of medicinal and aromatic plant sector from the beginnings. The Hungarian medicinal plant drug was a product of great demand on the world-market. However, the structural changes of agriculture in the beginning of the 90s had an adverse effect on the export activity of medicinal and aromatic plant sector, and the actual volume of the export is about one eight-tenth of the former one. The import of the medicinal plant was without importance and it was restricted only to the tropical species. Nowadays considerable amount of medicinal plant drugs are imported not only from the tropical countries but the former socialist countries, as well as from western countries where the price of the drug is cheaper due to the governmental subventions.
In the 80s there were only two companies (MEDIMPEX and Pharmatrade) with the government monopoly of export-import activity of medicinal and aromatic plants. After the closing down of this monopoly the number of firms dealing with export-import activity increased drastically. Now there is not any normative existing to determine the number of export-import firms, but their number decreased continuously, due to the regulating effect of the market. At the same time, some kind of product specialization appeared in this structural element of the sector.
Products made of medicinal and aromatic plants in the national market
The diversification of product made of medicinal and aromatic plants can be observed recently. It is going on either by the transformation of traditional product form, or by creation of new products (or new group of products). The most important actual groups containing medicinal and aromatic plant are shown in the figure.
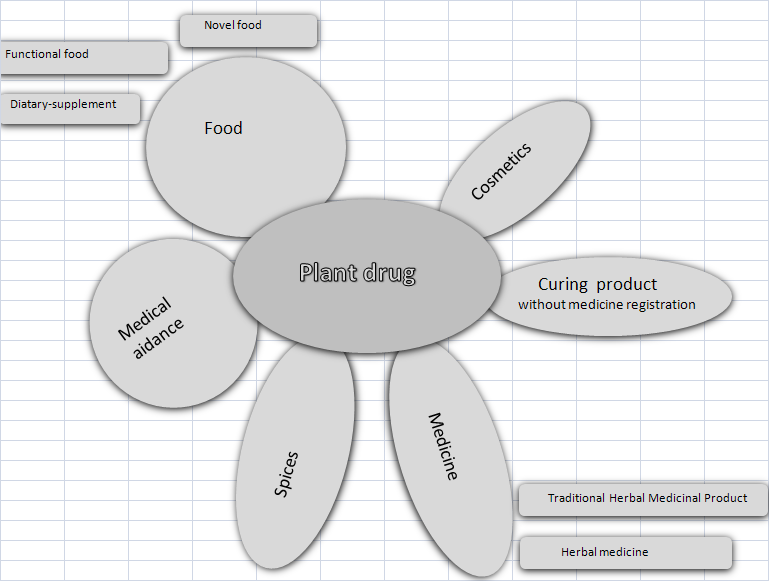
Main categories of products made of medicinal plants in the market
Products marketed as common foods
Medicinal plants appear more frequently in the market as food products. Different categories exist inside the food product. The simplest category is when the medicinal plant is sold similarly to the common teas. Such products are for instance the flower of chamomile and linden or leaf of peppermint representing diverse level of quality and packed in the tea bag. These products are present either on the shelves of shops specialized in botanicals or in common groceries, food marketing chains or in any other shops. The disadvantage of the products, which are sold in the form of tea, is that their quality is uncertain and even in the case of good product no curing indication are allowed to attach.
Dietary-supplements
In the last years we can meet larger and larger amounts of food-supplements in the market, whose composition and indications differ in a great deal and they belong to the category of food. A dietary supplement is a product taken orally that contains a "dietary ingredient" intended to supplement the diet. The ‘dietary ingredients’ in these products may include: vitamins, minerals, herbs or other botanicals, amino acids, and substances such as enzymes, organ tissues, glandulars, and metabolites. Dietary supplements can also be extracts or concentrates, and may be found in many forms such as tablets, capsules, soft gels, gel caps, liquids, or powders. They can also be in other forms, such as a bar, but if they are, information on their label must not represent the product as a conventional food or a sole item of a meal or diet. The number of dietary-supplements in both the national and international market increases continuously. During the last five years their number increased up to eight thousand.
Special foods
It is a worldwide tendency, that the food industry makes attempts to produce special foods and food combinations (healthy foods, functional foods etc.) by the processing of medicinal and aromatic plants, or by incorporating active agents, aromas, natural colorants isolated from these species. Based on the former estimates the Hungarian food industry, even in the 80s of the last century, about 52 aromatic plant species have been used for flavouring, aromatizing and colouring. Beyond these species further 20 natural aroma compounds were utilized in a relative large amount. From the utilized 52 plant species 31 species were cultivated ones and the drug of 10 species came from the wild by collection. The demand of food industry for natural colorants was about 20 tonnes. Furthermore, large amount of plant drug is utilized by the factories specialized in the production of soft or alcoholic drinks. They use about 30-35 different aromas, which can be purchased mainly from abroad.
Galenic products
The Galenic products (date back to the Roman times) represent a conventional form of medicinal and aromatic plants, which category compiles products of higher quality comparing to the dietary-supplements and foods. The Galenic products are present in many European countries and they are produced in pharmacies and in their special Galenic laboratories, using national or local recipes for preparation. These products are sold in the form of ‘species’ (tea or tea mixture), infusion (hot water extract), decoction (boiling with water), maceratum (cold water extract), tinctura (alcoholic extract) etc. The importance of conventional Galenic product decreased in the past decades because of the appearance of Galenic-like products made by pharmaceutical industries or enterprises specialized in production of plant medicines.
Curing product (without medicine registration)
Introduction of the category of curing product (without medicine registration) in 1987 was a great success of the Hungarian medicinal plant sector and created an up-to-date and controlled form of medicinal plant utilization. The establishment of this category was based on the world-wide biological, chemical, biochemical and pharmacological knowledge accumulated in the second half of the 20th century. The largest amount of products of this type was registered between 1992 and 1995 when about 60 products were introduced yearly. The spectrum of the products was relatively wide. According to the analysis of the composition of the products about 220 medicinal plant species and about 400 different drugs were utilized in their production process. The category of curing product in spite of the fact that they were conform with the overall requirements of efficacy, safety and quality – after the adherence to EU lost its former importance.
Traditional Herbal Medicinal Product
The creation and introduction of the category of Traditional Herbal Medicinal Product (THMP) had a negative impact on the innovation of goods belonging to the foregoing category of curing products (without medicine registration). In the former time, in the majority of European countries there was no, or only deficient regulation of the utilization of medicinal and aromatic plants. Because of this anarchic situation, under the aegis of EMA (European Medicine Agency) a directive 2004/24/EU on Traditional Herbal Medicinal Product was accepted. The directive was adapted by Hungary with the Decree of Hungarian Health Authority in 2005. By this regulation, the medicinal and aromatic plants and their products were sorted into the category of medicines. Consequently, the products of plant origin having any health claim can be traded as a category of medicine since 2011. The contradictions of the Directive accelerated different efforts to avoid its paragraphs. As an example, in France a special list of medicinal plants has been constructed for food shop marketing. In Finland, according to the present law, the THMP products can be sold in food shops. In many European countries – as an adverse effect of Directive – there are attempts to withdraw the medicinal plant drugs from the force of Pharmacopoeias. The medicinal plant drugs are put into the list of dietary-supplements or into the aliments. The European system seems to correspond much more to the former, less scientific American system. It means that in contrast to the original European goals, the utilization of medicinal plants starts to move to the less controllable application fields.
Medicine
The Hungarian Pharmaceutical Industry uses – even nowadays – active agents of plant origin or compounds which were synthesized from them. Because the compounds are isolated and structurally identified compounds, their official registration in going on under the same registration procedure which is applied in the case of synthetics. These products usually belong to the medicines of strong effect, they are subvented by National Health Care system and can be sold if the physician describes them. However, we have to mention that nowadays in Hungary the farmers only take place in production of poppy for production of raw of morphine. About 8-10 thousand hectares of poppy (Papaver somniferum) is cultivated yearly for the Hungarian morphine production.
Cosmetics and household-chemical products
The cosmetics and household industry utilize essential oils, mainly. Recently about 1400 different kinds of essential oils are produced on industrial scale worldwide. Unfortunately, the local production decreases continuously, and the fields of such traditional cultures as peppermint and lavender drive back to the unimportant areas. The recent economic-political changes did not favour this unfortunate phenomenon, which has started 15-20 years before.
Control questions:
Right answers